重建二叉树
1. 题目描述
输入某二叉树的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果,请重建出该二叉树。
2. 解题思路
- 前序遍历的第一个元素一定是树的根结点
- 在中序遍历中找到此节点,左边是左子树,右边是右子树
- 根据左右子树的长度,再次划分两个序列,进一步递归
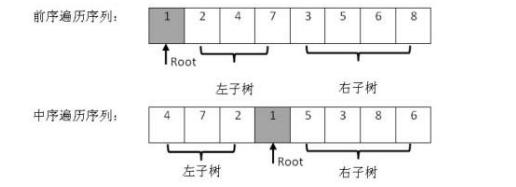
3. 代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
|
class Node {
constructor(value, left = null, right = null) {
this.value = value;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
function reConstruct(preorder, inorder) {
if (!preorder.length || !inorder.length) {
return;
}
let node = new Node(preorder[0]);
let i = 0;
for (; i < inorder.length; ++i) {
if (inorder[i] === preorder[0]) {
break;
}
}
node.left = reConstruct(preorder.slice(1, i + 1), inorder.slice(0, i));
node.right = reConstruct(preorder.slice(i + 1), inorder.slice(i + 1));
return node;
}
const preArr = [1, 2, 4, 7, 3, 5, 6, 8];
const midArr = [4, 7, 2, 1, 5, 3, 8, 6];
const binTree = reConstruct(preArr, midArr);
console.log(binTree);
|
判断是否子树
1. 题目描述
输入两棵二叉树 A 和 B,判断 B 是不是 A 的子结构。
树的节点定义如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
class Node {
constructor(value, left = null, right = null) {
this.value = value;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
|
2. 思路分析
假设判断的是p2是不是p1的子树,实现分为 2 个部分:
- 遍历树的函数
hasSubTree:遍历 p1 的每个节点,如果当前节点的 value 和 p2 根节点的 value 相同,立即进入判断函数(下一个函数);否则继续遍历
- 判断子树的函数
doesTree1HaveTree2:比较当前节点的值,再递归比较 p1 和 p2 的左右节点的值
3. 代码实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
|
function doesTree1HaveTree2(p1, p2) {
if (!p2) {
return true;
}
if (!p1 || p1.value !== p2.value) {
return false;
}
return (
doesTree1HaveTree2(p1.left, p2.left) &&
doesTree1HaveTree2(p1.right, p2.right)
);
}
function hasSubTree(p1, p2) {
let result = false;
if (p1 && p2) {
if (p1.value === p2.value) {
result = doesTree1HaveTree2(p1, p2);
}
if (!result) {
result = hasSubTree(p1.left, p2);
}
if (!result) {
result = hasSubTree(p1.right, p2);
}
}
return result;
}
const tree1 = new Node(0, new Node(1, new Node(3)), new Node(2));
const tree2 = new Node(1, new Node(3));
console.log(hasSubTree(tree1, tree2));
|
二叉树的镜像
1. 题目描述
请完成一个函数,输入一个二叉树,该函数输出它的镜像
2. 解题思路
书上给了一个示意图:
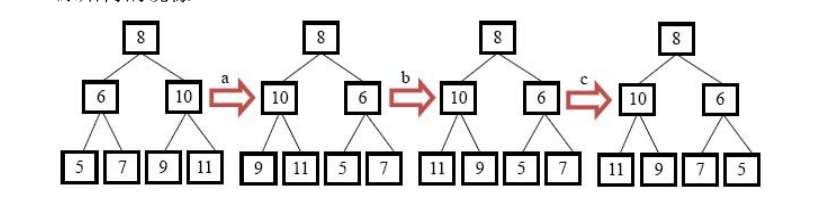
显而易见,从根节点开始,交换左右子树的位置;再照这个思路向下处理子树节点。
3. 代码实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
|
class Node {
constructor(value, left = null, right = null) {
this.value = value;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
function mirrorBinaryTree(root) {
if (root === null) {
return;
}
let left = root.left;
root.left = root.right;
root.right = left;
if (root.left) {
mirrorBinaryTree(root.left);
}
if (root.right) {
mirrorBinaryTree(root.right);
}
}
const root = new Node(0, new Node(1, new Node(3)), new Node(2));
mirrorBinaryTree(root);
console.log(root);
|
二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列
1. 题目描述
输入一个整数数组,判断该数组是不是某二叉搜索树的后序遍历的结果。如果是则返回 true,否则返回 false。假设输入的数组的任意两个数字都互不相同。
2. 思路描述
因为是后序遍历,所以根节点是最后一个元素。然后前面序列分为 2 部分,有一部分是左子树,有一部分是右子树。
根据二叉搜索树的性质,左子树的元素一定小于最后一个元素,右子树的元素一定大于最后一个元素。
根据这个思路,一直递归下去即可。只要所有部分都满足二叉搜索树的性质,那么符合条件。
3. 代码实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
|
function isBST(tailOrder) {
if (tailOrder.length === 0) {
return true;
}
const length = tailOrder.length;
let root = tailOrder[length - 1],
i,
j;
for (i = 0; i < length - 1 && tailOrder[i] < root; ++i);
for (j = i; j < length - 1 && tailOrder[j] > root; ++j);
if (j !== length - 1) {
return false;
}
let left = isBST(tailOrder.slice(0, i));
let right = isBST(tailOrder.slice(i, length - 1));
return left && right;
}
console.log(isBST([5, 7, 6, 9, 11, 10, 8]));
console.log(isBST([4, 3, 2, 1]));
console.log(isBST([7, 4, 6, 5]));
|
二叉树中和为某一值的路径
1. 题目描述
输入一棵二叉树和一个整数,打印出二叉树中结点值的和为输入整数的所有路径。从树的根结点开始往下一直到叶结点所经过的结点形成一条路径。
2. 思路分析
- 每次来到新的节点,记录新节点信息
- 检查新节点是否是叶子节点,如果是,判断路径上的节点值总和是否符合条件;如果不是,继续递归处理左右子树,回到第 1 步
- 最后需要将新节点的信息移除
3. 代码实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
|
class Node {
constructor(value = 0, left = null, right = null) {
this.value = value;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
function findPath(root, target) {
const paths = [];
let sum = 0;
function _findPath(node, path) {
if (node === null) {
return;
}
sum = sum + node.value;
path.push(node);
const isLeaf = node.left === null && node.right === null;
if (isLeaf && sum === target) {
paths.push([...path]);
}
if (node.left !== null) {
_findPath(node.left, path);
}
if (node.right !== null) {
_findPath(node.right, path);
}
sum = sum - node.value;
path.pop(node);
}
_findPath(root, []);
return paths;
}
const root = new Node(1, new Node(2), new Node(3, null, new Node(-1)));
console.log(findPath(root, 3));
|
二叉树层序遍历
1. 题目描述
从上往下打印出二叉树的每个结点,同一层的结点按照从左到右的顺序打印。
2. 思路分析
借助队列这种“先入先出”的线性数据结构即可。每次访问队列中的元素的时候,输出它的值,并且将其非空左右节点放入队列中。直到队列为空,停止输出,结束函数循环即可。
3. 代码实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| class TreeNode {
constructor(value, left = null, right = null) {
this.value = value;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
function levelTravel(root) {
const queue = [root];
while (queue.length) {
let first = queue.shift();
console.log(first.value);
if (first.left) {
queue.push(first.left);
}
if (first.right) {
queue.push(first.right);
}
}
}
const root = new TreeNode(
10,
new TreeNode(6, new TreeNode(4), new TreeNode(8)),
new TreeNode(14, new TreeNode(12), new TreeNode(16))
);
levelTravel(root);
|
二叉树转双向链表
1. 题目描述
输入一棵二叉搜索树,将该二叉搜索树转换成一个排序的双向链表。要求不能创建任何新的结点,只能调整树中结点指针的指向。
2. 思路分析
在搜索二叉树中,左子结点的值总是小于父结点的值,右子结点的值总是大于父结点的值。因此我们在转换成排序双向链表时,原先指向左子结点的指针调整为链表中指向前一个结点的指针,原先指向右子结点的指针调整为链表中指向后一个结点指针。
因为要遍历树,所以要选取遍历算法。为了保证遍历的有序性,采用中序遍历。在 convertNode 函数实现中,注意 lastNodeInList 语意,剩下的按照思路写出来即可。
3. 代码实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
| class TreeNode {
constructor(value, left = null, right = null) {
this.value = value;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
function convertNode(node, lastNodeInList = null) {
if (!node) {
return null;
}
if (node.left) {
lastNodeInList = convertNode(node.left, lastNodeInList);
}
node.left = lastNodeInList;
if (lastNodeInList) {
lastNodeInList.right = node;
}
lastNodeInList = node;
if (node.right) {
lastNodeInList = convertNode(node.right, lastNodeInList);
}
return lastNodeInList;
}
function convertTreeToList(root) {
let lastNodeInList = convertNode(root);
let headOfList = lastNodeInList;
while (headOfList && headOfList.left) {
headOfList = headOfList.left;
}
return headOfList;
}
const root = new TreeNode(
10,
new TreeNode(6, new TreeNode(4), new TreeNode(8)),
new TreeNode(14, new TreeNode(12), new TreeNode(16))
);
let nodeOfList = convertTreeToList(root);
while (nodeOfList) {
console.log(nodeOfList.value);
nodeOfList = nodeOfList.right;
}
|
判断是否是平衡二叉树
1. 题目描述
判断一棵树是不是平衡二叉树。
2. 思路分析
思路一:计算出左右子树的深度,然后检查差。递归继续判断左子树和右子树是不是平衡二叉树。
思路二:先计算左子树和右子树是不是平衡二叉树,然后再计算本身是不是平衡二叉树。
关于思路二为什么能比思路一更好,请看代码。
3.1 代码实现 - 树的深度
先递归实现树的深度函数:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| class Node {
constructor(value, left, right) {
this.value = value;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
function treeDepth(root) {
if (!root) {
return 0;
}
const leftDepth = treeDepth(root.left);
const rightDepth = treeDepth(root.right);
return leftDepth > rightDepth ? leftDepth + 1 : rightDepth + 1;
}
|
3.2 思路一
这种思路慢是因为:节点被重复计算了。得出 leftDepth 计算了一遍 root.left ,最后还要再调用自身计算 root.left。尤其是叶子节点,会造成很多的计算浪费。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
function isBalanced(root) {
if (!root) {
return true;
}
const leftDepth = treeDepth(root.left);
const rightDepth = treeDepth(root.right);
const diff = Math.abs(leftDepth - rightDepth);
if (diff > 1) {
return false;
}
return isBalanced(root.left) && isBalanced(root.right);
}
|
3.3 思路二
先遍历和计算左右子树,最后计算本身。不需要重复计算。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
function isBalanced2(root, obj = {}) {
if (!root) {
obj.depth = 0;
return true;
}
const left = {},
right = {};
if (isBalanced2(root.left, left) && isBalanced2(root.right, right)) {
const diff = Math.abs(left.depth - right.depth);
if (diff > 1) {
return false;
}
obj.depth = 1 + (left.depth > right.depth ? left.depth : right.depth);
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
|
3.4 测试
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
const root = new Node(
1,
new Node(2, new Node(4), new Node(5, new Node(7))),
new Node(3, null, new Node(6))
);
console.log(treeDepth(root));
console.time();
console.log(isBalanced(root));
console.timeEnd();
console.time();
console.log(isBalanced2(root));
console.timeEnd();
|

