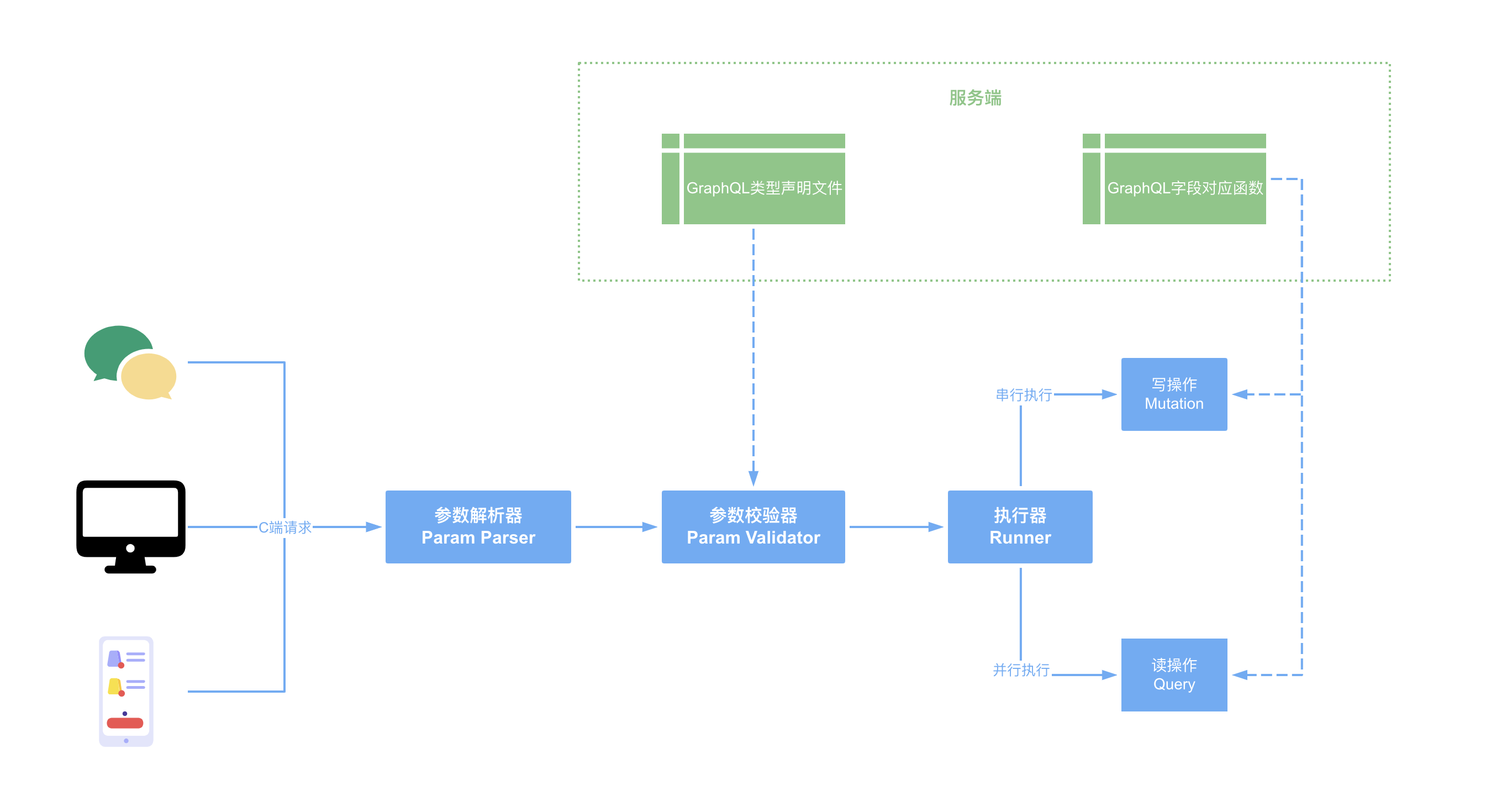
什么是 GraphQL? 它是一种 api 查询语言。使用者按照规范描述数据结构,可以来获取所需数据;开发者需要做的是编写获取数据的响应函数,以及声明查询字段的类型。
GraphQL 的用途 主要用于查询和聚合数据。开发者只需要声明查询字段类型,以及每个字段数据的获取函数。前端通过 graphql 语法,获取自己想要的任何字段。
这样就不需要每个字段或者新的业务模块数据,再开一个 restful api,所有的查询都收到一个接口中。
GraphQL 和 Restful API 最初的时候,很多人觉得是替代 restful api。现在多是和 restful api 配合使用。举 2 个例子。
第一个例子,GraphQL 更多的用于查询和聚合数据,也就是“读”的场景。而更改数据大多数是敏感操作,还会涉及鉴权、缓存、节流等复杂逻辑,一般都封装单独的 restful api 来给前端调用。
第二个例子,GraphQL 以 Restful API 的方式暴露给前端使用。例如在腾讯云 CVM 控制台中,打开 Console -> Network,搜索 graphql 关键字就能看到请求。这个请求就是一个支持 graphQL 查询的 restful API。在实际开发中,可以根据业务模块,抽出不同的支持 graphQL 的 restful api,方便维护;也可以将其放入一个大的 restful api 中。
代码实战 npm 配置文件 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 { "scripts" : { "test" : "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1" , "dev" : "nodemon -e graphql,js ./www.js" } , "author" : "xin-tan.com" , "license" : "ISC" , "dependencies" : { "@graphql-tools/graphql-file-loader" : "^6.2.7" , "@graphql-tools/load" : "^6.2.8" , "axios" : "^0.21.1" , "express" : "^4.17.1" , "express-graphql" : "^0.12.0" , "graphql" : "^15.5.0" } }
GraphQL 类型声明 对于 graphql,开发需要声明查询字段的类型。例如:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 type User { name : String age : Int } type Duck { weight : Float color : String owner : User description( id : String! ) : String } type Query { hello : String author : User getUser( name : String! ) : User getAllUsers : [ User] getDuck( id : String! ) : Duck } input UserInput { name : String age : Int } type Mutation { createUser( userInfo : UserInput) : User updateUser( userInfo : UserInput) : User }
GraphQL 获取数据函数 规定了数据类型之后,会定义对应的数据字段的获取逻辑。例如:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 const userMap = { author : { name : "author" , age : 23 , }, user1 : { name : "user1" , age : 18 , }, }; const duckMap = { 0 : { weight : 1 , color : "green" , owner : userMap.author , description : ({ id } ) => { return `I am duck, my info is ${JSON .stringify(duckMap[id])} ` ; }, }, }; const root = { hello : () => "Hello world!" , author : () => { return userMap.author ; }, getUser : ({ name } ) => { return userMap[name]; }, getAllUsers : () => { const users = []; for (let name in userMap) { users.push (userMap[name]); } return users; }, getDuck : ({ id } ) => { return duckMap[id]; }, createUser : ({ userInfo } ) => { userMap[userInfo.name ] = userInfo; console .log (">>> invoke createUser mutation" ); return userInfo; }, updateUser : ({ userInfo } ) => { if (!userMap[userInfo.name ]) { throw new Error (`Please create user ${userInfo} ` ); } userMap[userInfo.name ].age = userInfo.age ; console .log (">>> invoke updateUser mutation" ); return userInfo; }, }; module .exports = { root, };
前端传入查询语句,字段会自动匹配根对象对应的函数。下面的查询语句,就会执行 root.hello() 函数,并且返回结果。
1 2 3 query RootQuery { hello }
注意:query 中的字段也可以实现数据更新逻辑,但按照推荐,任何涉及数据更新的改动,都应该放入到 mutation 中。
提供 GraphQL 访问服务 方法 1:通过 buildSchema 直接构建 schema。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 const { buildSchema } = require( "graphql" ) ; const schema = buildSchema( ` type Query { hello : String name : String } `) ; const app = express( ) ; app.use( "/graphql" , graphqlHTTP( { rootValue : root, // root 就是上面的 root 对象 schema , graphiql : true , } ) ) .listen( 4000 , ( ) = > console.log( "Now browse to http://localhost:4000/graphql" ) ) ;
这么写的缺陷就是 graphql 字段声明放在了 js 文件中,编辑器没法高亮+格式化,也不方便单独维护。随着字段增多,js 文件会变得非常冗长。
方法 2:使用 graphql 配套的工具库
这些工具库支持读取 graphql 文件,也支持模块化预发,并且将其加载进来。
例如方法 1 的 GraphQL 类型声明,就可以将其放入root.graphql文件中,然后读取并加载。
1 2 3 4 5 6 const { loadSchema, loadSchemaSync } = require ("@graphql-tools/load" );const { GraphQLFileLoader } = require ("@graphql-tools/graphql-file-loader" );const schema = loadSchemaSync ("./graphql/root.graphql" , { loaders : [new GraphQLFileLoader ()], });
编写 GraphQL 查询语句 读的操作都在 Query 中,写的操作都在 Mutation 中。
前端在使用的时候,查询语句如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 query RootQuery { hello getAllUsers { name age } getUser( name : "user1" ) { name age } getDuck( id : "0" ) { weight color owner { name } description( id : "0" ) } } mutation CreateUser3 { user3 : createUser( userInfo : { name : "user3" , age : 30 } ) { name age } user4 : createUser( userInfo : { name : "user4" , age : 30 } ) { name } updateUser( userInfo : { name : "user3" , age : 40 } ) { name age } }
其中,mutation 中写操作是串行的,query 中读操作是并发的。可以给 mutation 或者 query 起名字,也可以给返回结果起别名(例如 CreateUser3 中的 user3)。
参考链接